rtpengine rhel 9 libspan OKey repo
git clone https://github.com/sipwise/rtpengine.git
cd rtpengine
#check Version in spec file
#check latest commit by “git log”.
el/build-with-mock.sh 14.1.0.0+0~mr14.1.0.0 d1c235cbd295e595a3e12e466224224661684a60
mock -r el/rtpengine-9-x86_64.cfg rpmbuild/SRPMS/ngcp-rtpengine-14.1.0.0+0~mr14.1.0.0-1.el9.src.rpm
Okay repo:
dnf install http://repo.okay.com.mx/centos/9/x86_64/release/okay-release-1-11.el9.noarch.rpm
Install Rocky 9 from minimal ISO
https://www.rockylinux.org/download/
Download ISO:
wget https://download.rockylinux.org/pub/rocky/9/isos/x86_64/Rocky-9.3-x86_64-minimal.iso
Type repo address:
download.rockylinux.org/pub/rocky/9/BaseOS/x86_64/os
Issue: No sound between Rocky 9 and windows RDP client:
you have to add sound module by compiling and install it, in my case it works smoothly. (source)
cd /home
git clone https://github.com/neutrinolabs/pipewire-module-xrdp.git
dnf install git gcc make autoconf libtool automake pkgconfig
dnf install pipewire-devel
./bootstrap
./configure
make
make install
reboot
Issue: Keyboard layout. After reconnect sometime you can not change layout. (source)
Fast way to restore is change “Type Special Characters” in “Settings” to any other. After that switching between layers will be fine.
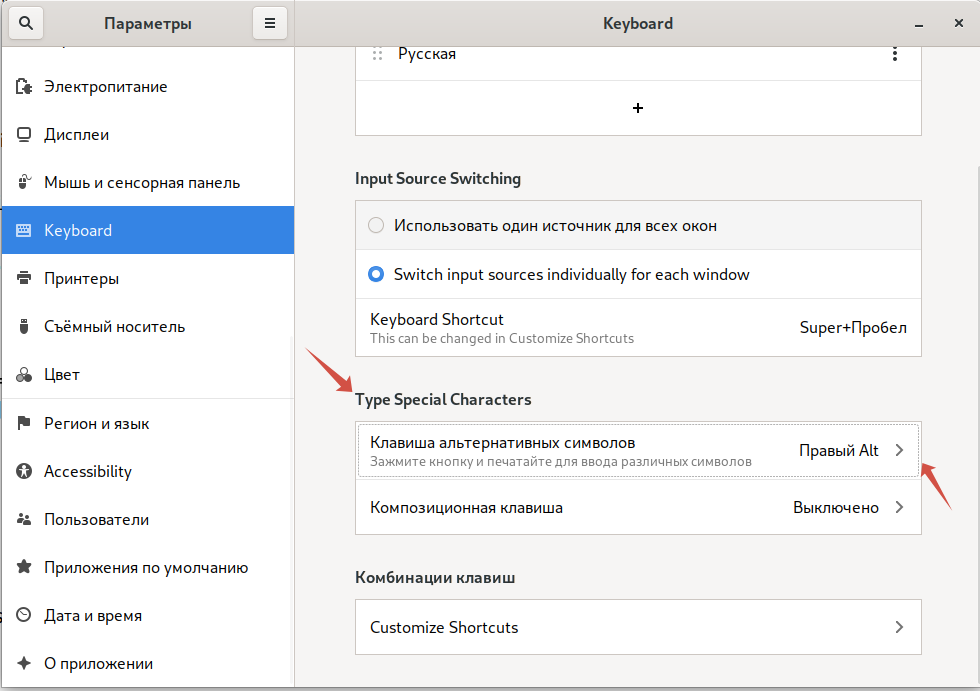
Try to change xrdp-keyboard.ini like this:
Edit xrdp_keyboard.ini like this. This will override "us" by "us,ru".
--- xrdp_keyboard.ini.orig 2016-03-08 13:49:27.488775742 +0900
+++ xrdp_keyboard.ini 2016-03-08 13:51:24.972745599 +0900
@@ -74,7 +74,7 @@
# <rdp layout name> = <X11 keyboard layout value>
[default_layouts_map]
-rdp_layout_us=us
+rdp_layout_us=us,ru
rdp_layout_de=de
rdp_layout_fr=fr
rdp_layout_it=it
If you want to use "us,ru" instead of "ru" in case you specify Russian in client, like this.
--- xrdp_keyboard.ini.orig 2016-03-08 13:49:27.488775742 +0900
+++ xrdp_keyboard.ini 2016-03-08 13:52:33.092750998 +0900
@@ -82,7 +82,7 @@
rdp_layout_jp2=jp
rdp_layout_jp3=jp
rdp_layout_jp4=jp
-rdp_layout_ru=ru
+rdp_layout_ru=us,ru
rdp_layout_se=se
rdp_layout_ch=ch
rdp_layout_pt=pt Rocky 9 opensips 3.4 fresh install
You have to enable some repo and add epel repository if you wish to install ALL modules from opensips repo.
ADD EPEL:dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm
dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-next-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm
Enable CRB:dnf config-manager --set-enabled crb
ADD opensips repo from official sire opensips.org:dnf install https://yum.opensips.org/3.4/releases/el/9/x86_64/opensips-yum-releases-3.4-6.el9.noarch.rpm
Install by:dnf install opensips*
oracle 8 linux. rtpengine 11.2 with uek kernel
There are some specific TIPS for ORACLE linux 8 and UEK core for compiling\installing rtpengine.
for test vanilla server i will use oracle 8 linux:
take ISO from: https://yum.oracle.com/oracle-linux-isos.html
set http repository: http://yum.oracle.com/repo/OracleLinux/OL8/baseos/latest/x86_64
INSTALL RTPENGINE 11.2.2.0
git clone https://bitbucket.org/yooxy/centos8-rtpengine10-all-codecs.git cd centos8-rtpengine10-all-codecs #use precompiled pkgs from RPMS/el8/ and RPMS/el8/11 dirs dnf -y install epel-release dnf config-manager --set-enabled ol8_codeready_builder dnf -y install --nogpgcheck https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/el/rpmfusion-free-release-8.noarch.rpm dnf install kernel-uek-devel cd RPMS/el8 dnf localinstall ffmpeg-libs-4.2.7-1.el8.x86_64.rpm libavdevice-4.2.7-1.el8.x86_64.rpm cd 11 dnf localinstall ngcp-rtpengine-11.2.2.0+0~mr11.2.2.0-1.el8.x86_64.rpm ngcp-rtpengine-kernel-11.2.2.0+0~mr11.2.2.0-1.el8.x86_64.rpm ngcp-rtpengine-dkms-11.2.2.0+0~mr11.2.2.0-1.el8.noarch.rpm
INSTALL UEK KERNEL
We will using UEK 5.4.17. check “uname -a” maybe you already have 5.4.17 kernel, if not:
dnf config-manager --disable ol8_UEKR7 dnf config-manager --enable ol8_UEKR6 dnf install kernel-uek kernel-uek-devel reboot
SIGN MODULE ORACLE 8
Issue “Key was rejected by service” may happens if you have enabled “Secure boot”.
To check it: run “mokutils –sb-state”. In enabled state you have to sign your rtpengine module for kernel. To add your key do this:
mokutil –import /var/lib/dkms/mok.pub
enter password you wish, and after reboot you see in BOIS invitation to enroll your keys. do it with password you have entered before and then xt_rtpengine module will be loaded correctly.
ISSUES:
If you have installed UEK 5.15+ then you have to update you GCC compiler to 11+ or you will have error when compiling kernel module for rtpengine: you are using 11.5 GCC for compiling kernel and 8.5 for compiling xt_rtpengine.
modprobe: FATAL: Module xt_RTPENGINE not found in directory
Extension RTPENGINE revision 0 not supported, missing kernel module?
ERR: [core] FAILED TO CREATE KERNEL TABLE 0 (No such file or directory), KERNEL FORWARDING DISABLED
dkms (kernel) module xt_RTPENGINE not compiled at all.
in common cases you have to install kernel-uek-devel-<version>, where version is “uname -r”
RTPENGINE cluster TIPS
There main concept here: https://github.com/sipwise/rtpengine/wiki/Redis-keyspace-notifications
but few important thing to check:
1. Redis have disabled keyspace notification to enable change to notify-keyspace-events “AKE” in redis.conf
2. interface names should start exactly from “pub”
3. If you have not active interface IP on passive (pub2) rtpengine you have to set sysctl net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind=1
| Posted in opensips, rtpengine | No Comments »
cli sip client
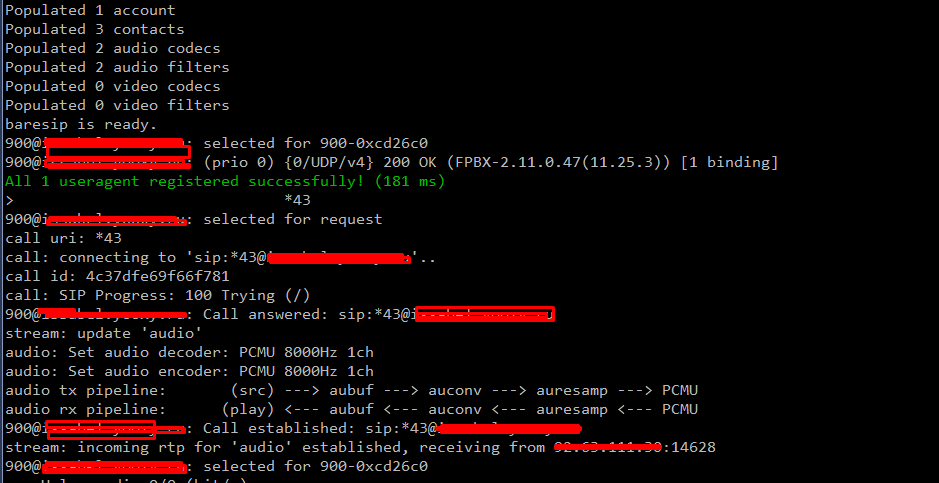
simple (1 minute) way to install and make test sip from command line
how baresip works:
when you run: “baresip -f cofnig_dir” it will create dir config_dir with default files
then yo have to add accouns into config_dir/accounts, change everything you need into config_dir/config
then you may run again: “baresip -f cofnig_dir”
you will see console from basresip
then you have to use commands like “d” with means call to SIP uri
for example “d” and *43 will send call from your account to same domain with *43 (echo test for asterisk).
yum install baresip cd /root baresip -f baresip_config #press ESC echo"<sip:900@asterisk_ip>;auth_pass=testpassword" >> baresip_config/accounts/accounts change port in baresip_config/config from 5060 to 5099 for example baresip -f baresip_config #press "d" type *43 or full sip uri "111@newhost"
Duplicity. centos 7.
#scrip for compile and install duplicity from gitlab yum install git epel-release -y yum install python3-pip python3-devel librsync-devel gcc -y git clone https://gitlab.com/duplicity/duplicity.git cd duplicity/ pip3 install --upgrade pip pip3 install -r requirements.txt python3 setup.py install11.10.2022
TIPS for rpm, rpmbuild, yum
The main reason for me to use rpmbuild when i compile and install any software is that you can easily install and remove all files. In “make” case some time you can not do that by command “make remove”. Also when you are using “yum install” than installed libraries can be used by other software for solve dependencies.
Check installed files for certain package:
rpm -ql ffmpeg-libs
TIPs for create spec files:
(rus) https://blog.korphome.ru/2014/11/18/centos-собираем-пакеты-при-помощи-rpmbuild/
(eng) https://rpm-packaging-guide.github.io/#files
Rtpengine. Opus. Ilbc.
I am using ilbc to make calls with mobile applications. As we know ilbc is old codec, all tests,table and pictures all over the net make us feel as ilbc most worse then opus. because opus is faster, more quality e.t.c.
Seems… my opinion is different, if you want good quality and minimum bandwidth out of box then use ilbc – it’s not problem, it will have 23kb bandwidth for one side. Audio bandwidth up to 4kHz so voice will be good enough for conversation. But there is no way to reduce bitrate and bandwidth with ilbc, so let’s try to implement opus.
also, converting 48kHz(sample rate) files with libopus is slowest then with ilbc in most of cases. Be noted that you can not use opus with 8kHz(sample rate) in default configuration by rtpengine only 48kHz is supported.
Components used for testing:
- centos 7: iftop, tcpdump
- custom ffmpeg 4.2.7,
- opus 1.3.2,
- opus-tools: opusenc, opusrtp
- rtpengine 11.0.1.5,
- microsip 3,
- sipp 3.6.
- clumsy ( simulate bad network on windows)
I will start from end, maybe it will be helpful for someone. What was my aim, i wanted to use packet loss, fec, speech mode, low bandwidth from opus codec.
Success:
* low bandwidth with 8kb\s bitrate (13kb\s actual) and 40ms frame duration.
Failed:
* packet_loss (no way to understand if it really works, real test does not show that it helps)
* fec, ( same as packet loss)
* speech mode, (take more cpu resources when encoding without real result)
How to add opus support into rtpengine.
For encoding\decoding opus rtpeginge using ffmpeg library. so you have to be sure that libopus is present with ffmpeg. you can do that with: “ffmpeg -h encoder=libopus” if you don’t see: “Codec ‘libopus’ is not recognized by FFmpeg.” then seems ffmpeg have opus with libopus encoder\decoder.
How to set parameters for opus codec:
when you do rtpengine_offer use this: as one of params:
codec-transcode-opus/48000/2/8000/40/maxaveragebitrate–8000;maxplaybackrate–12000;useinbandfec–1;ptime–40;maxptime–40/ar-48000,b–8000
where is :
48000 – sample rate in SDP
2 – channels (default for opus)
8000 (b\s) – bitrate for codec implement on encoder side
40 (ms) – frame duration (should affect on encoder side, but you have a=ptime 20 in SDP, codec will work on 20 ms)
“maxaveragebitrate–8000;maxplaybackrate–12000;useinbandfec–1;ptime–40;maxptime–40” there are a=fmtp parameters into SDP, you can check what it means in RFC.
“ar–48000,b–8000” – codec individual options you can take a look ffmpeg docs to check what you can use. For some reason individual options for opus codec like packet_loss can not be set by this logic, you have to set it inside codeclib.c in rtpengine source code . for example “
if (enc->ptime > 0 ) {
codeclib_set_av_opt_int(enc, "frame_duration", enc->ptime);
codeclib_set_av_opt_int(enc, "packet_loss", 5);
codeclib_set_av_opt_int(enc, "fec", 1);
codeclib_set_av_opt_int(enc, "application", 2048);
}
issues: when you set 40 ms frame_duration for opus and you have not any a=ptime 40 in SDP towards to destination peer, peer will not send stream with 40 ms frame_duration, maybe there is a bug into Microsip. Using ptime and maxptime into codec options – not helps.
so, to avoid this i did add ptime=40 as rtpengine_offer parameter and add little fix to codeclib.c to make 40ms default ptime for opus codec.
How to check speed of converting with libopus
you need any music input file, for example any.wav. then you may try to use
“ffmpeg -i madonna-48k.wav -c libopus -ab 18000 madonna.opus“
it will convert wav file to opus with bitrate 18k\s
as result you will see some data ended with
“size= 82kB time=00:00:39.83 bitrate= 16.8kbits/s speed= 136x”
also you can convert it with libilbc encoder:
“ffmpeg -i madonna-48k.wav -c libilbc -ar 8000 -ab 18000 madonna.lbc“
you will see:
“size= 74kB time=00:00:39.84 bitrate= 15.2kbits/s speed= 170x“
to be continued….
16.08.2022Oracle Centos 8. Rtpengine with all codecs supported.
As result of this instruction you will have all this codecs supported in your centos 8 installations.
PCMA: fully supported
PCMU: fully supported
G723: fully supported
G722: fully supported
G729: fully supported
G729a: fully supported
speex: fully supported
GSM: fully supported
iLBC: fully supported
opus: fully supported
AMR: fully supported
AMR-WB: fully supported
telephone-event: fully supported
CN: fully supportedSynopsis:
RPMS, build and install scripts: git clone https://bitbucket.org/yooxy/centos8-rtpengine10-all-codecs.git
This instruction will give you RTPENGINE for Centos 7 and Centos 8 withh all codecs. RPM packages in RPMS dir are ready for install. But also you have rpmbuild-rtpengine.el7 and rpmbuild-rtpengine.el8 to compile it on your system in automatically way.
if you start to compiling on new system, then everything should go fine after you type sh rpmbuild-rtpengine.el7.
IF you work on production system , then check files you are running before start due to you may to install unnecessary packets or kernels.
To build rtpengine with all codecs (g729,AMR,opus,iLBC, GSM) on Centos 8:
cd ~
git clone https://bitbucket.org/yooxy/centos8-rtpengine10-all-codecs.git
sh rpmbuild-rtpengine.el8
cd ~/rpmbuild/RPMS/
dnf install noarch/ngcp-rtpengine-dkms-10.5.1.3+0~mr10.5.1.3-1.el8.noarch.rpm x86_64/ngcp-rtpengine-kernel-10.5.1.3+0~mr10.5.1.3-1.el8.x86_64.rpm x86_64/ngcp-rtpengine-10.5.1.3+0~mr10.5.1.3-1.el8.x86_64.rpmYour RPMs ready for install in ~/root/rpmbuild/RPMS
To install rtpengine without build 10.5 run “sh install-rtpengine.el7”
| Posted in Без рубрики, Готовые решения | No Comments »
| Posted in Uncategorized | No Comments »